使用 PowerShell 檢查打開(偵聽)端口
在 PowerShell 中,您可以使用測試網連接cmdlet 用於檢查遠程計算機上的端口是否可用(打開)。您可以使用此 cmdlet 檢查遠程服務器或網絡服務的響應和可用性、測試 TCP 端口是否被防火牆阻止、檢查 ICMP 可用性和路由。實際上,Test-NetConnection取代了幾種流行的網絡管理工具,例如ping,tracert,telnet,pathping、TCP端口掃描器等
內容:
- 使用 Test-NetConnection 檢查打開的 TCP 端口
- PowerShell:檢查多個主機上的開放端口
- PowerShell 中的簡單 TCP/IP 端口掃描器
- 如何使用 PowerShell 列出 Windows 上的開放端口
使用 Test-NetConnection 檢查打開的 TCP 端口
您可以使用 Test-NetConnection cmdlet 僅檢查 TCP 端口。例如,要檢查遠程郵件服務器上的 TCP 端口 25(SMTP 協議)是否打開:
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName ny-msg01 -Port 25
筆記。您可以使用 Test-NetConnection cmdlet 僅測試 TCP 端口連接。但是,您無法使用 cmdlet 檢查遠程 UDP 端口的可用性。
Test-NetConnection 命令具有別名跨國公司。同一命令的簡化版本如下所示:
TNC ny-msg01 -Port 25
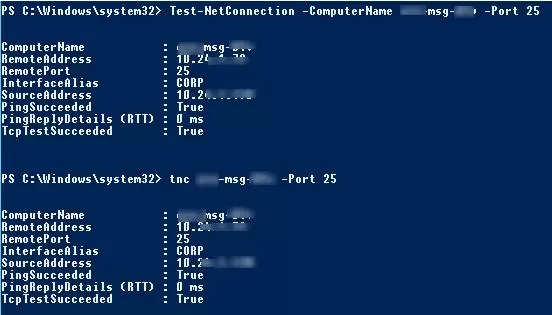
我們看一下命令的結果:
ComputerName : ny-msg01 RemoteAddress : 10.20.1.7 RemotePort : 25 InterfaceAlias : CORP SourceAddress : 10.20.1.79 PingSucceeded : True PingReplyDetails (RTT) : 0 ms TcpTestSucceeded : True
如您所見,cmdlet 將服務器名稱解析為 IP 地址,檢查 ICMP 響應(類似於ping),並檢查來自 TCP 端口的響應(端口可用性)。指定的服務器通過 ICMP 響應(PingSucceeded = True)並且 TCP 端口 25 已打開(RemotePort=25, TcpTestSucceeded= True)。
筆記。如果該命令返回 PingSucceeded=False 且 TcpTestSucceeded=True,這很可能意味著 ICMP Echo 請求 (ping) 在遠程計算機上被禁用。
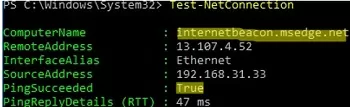
如果您運行不帶參數的 Test-NetConnection,它將檢查計算機是否已連接到互聯網(檢查網絡的可用性)internetbeacon.msedge.net主持人)。

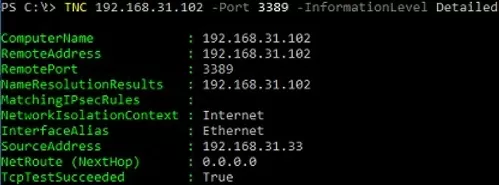
您可以添加 –信息等級詳細檢查遠程 TCP 端口時顯示詳細信息的選項:
TNC 192.168.32.101 -Port 3389 -InformationLevel Detailed

該 cmdlet 有一個特殊參數 –通用TCP端口,它允許您指定已知網絡協議的名稱(HTTP、RDP、SMB、WINRM)。
例如,要檢查 HTTP Web 服務器的可用性,您可以使用以下命令:
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName woshub.com -CommonTCPPort HTTP
或者檢查默認 RDP 端口 (TCP/3389) 的可用性:
Test-NetConnection ny-rds1 –CommonTCPPort RDP
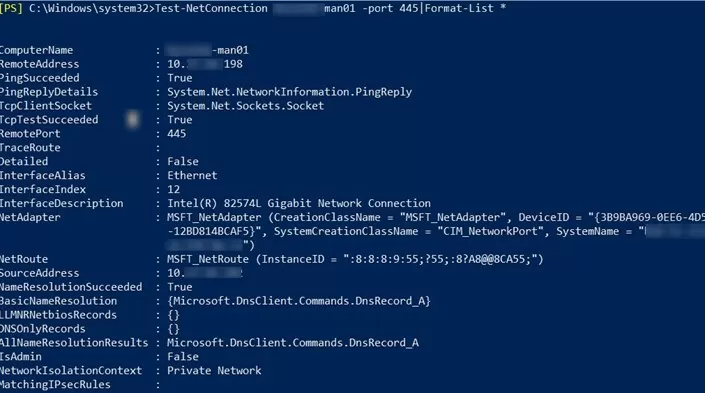
您可以列出 Test-NetConnection cmdlet 返回的所有參數:
Test-NetConnection ny-man01 -port 445|Format-List *

如果您只需要查看端口是否可用,可以更快地檢查:
TNC ny-msg1 -Port 25 -InformationLevel Quiet
該 cmdlet 返回True,這意味著遠程 TCP 端口已打開。
![]()
![]()
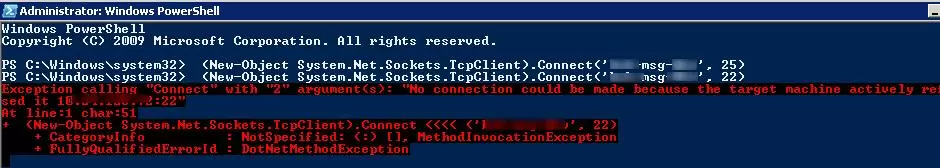
提示。在早期版本的 Windows PowerShell(版本 4.0 之前)中,您可以使用以下命令檢查遠程 TCP 端口的可用性:
(New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TcpClient).Connect('ny-msg01', 25)

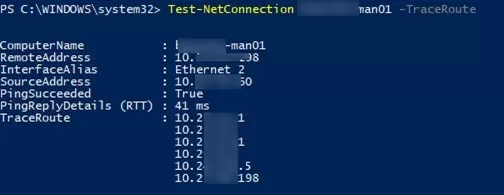
您可以使用 Test-NetConnection cmdlet 來跟踪到遠程服務器的路由 -追踪路由參數(類似於內置tracertWindows 中的命令)。您可以使用以下命令限制路由檢查期間的最大跳數-酒花範圍。
Test-NetConnection ny-man01 –TraceRoute
Cmdlet 返回以毫秒為單位的網絡訪問延遲摘要(PingReplyDetails (RTT): 41 ms)以及通往目標主機途中的所有路由器的 IP 地址。

您可以使用 PowerShell 檢查多台遠程計算機上特定端口的可用性。將主機名或 IP 地址列表保存在純文本文件中,名稱為servers.txt。
例如,您的任務是在服務器列表中查找 TCP/25 端口沒有響應或關閉的主機:
Get-Content c:PSlist_servers.txt | where { -NOT (Test-Netconnection $_ -Port 25 -InformationLevel Quiet)}| Format-Table -AutoSize
您可以使用簡單的監視 PowerShell 腳本來檢查遠程服務器的可用性,並在任何服務器不可用時顯示彈出通知。
例如,您可以在 AD 健康檢查期間檢查所有域控制器上基本服務的可用性(可以使用 Get-ADDomainController cmdlet 獲取 DC 列表)。讓我們檢查 DC 上的以下服務(PortQry 工具中有類似的“域和信任”規則):
- RPC – TCP/135
- LDAP – TCP/389
- LDAP – TCP/3268
- DNS – TCP/53
- Kerberos – TCP/88
- 中小企業-TCP/445
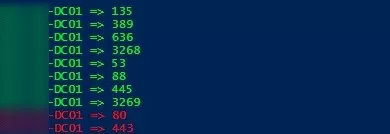
$Ports = "135","389","636","3268","53","88","445","3269", "80", "443"
$AllDCs = Get-ADDomainController -Filter * | Select-Object Hostname,Ipv4address
ForEach($DC in $AllDCs){
Foreach ($P in $Ports){
$check=Test-NetConnection $DC.Ipv4address -Port $P -WarningAction SilentlyContinue
If ($check.tcpTestSucceeded -eq $true)
{Write-Host $DC.hostname $P -ForegroundColor Green -Separator " => "}
else
{Write-Host $DC.hostname $P -Separator " => " -ForegroundColor Red}
}
}
該腳本會檢查域控制器上指定的 TCP 端口,如果有任何端口不可用,則會以紅色突出顯示它們(您可以將此 PowerShell 腳本作為 Windows 服務運行)。

PowerShell 中的簡單 TCP/IP 端口掃描器
您可以使用 PowerShell 實現簡單的 IP 掃描器,掃描遠程主機或 IP 子網以查找打開/關閉的 TCP 端口。
要掃描 192.168.1.100 和 192.168.1.150 之間的 IP 地址範圍並顯示打開端口 3389 的計算機:
foreach ($ip in 100..150) {Test-NetConnection -Port 3389 -InformationLevel "Detailed" 192.168.1.$ip}
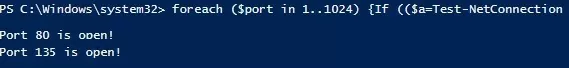
掃描遠程主機上的一系列 TCP 端口(從 1 到 1024):
foreach ($port in 1..1024) {If (($a=Test-NetConnection srvfs01 -Port $port -WarningAction SilentlyContinue).tcpTestSucceeded -eq $true){ "TCP port $port is open!"}}

如何使用 PowerShell 列出 Windows 上的開放端口
使用獲取 NetTCPConnectioncmdlet 列出本地計算機上打開的端口(這相當於 PowerShellNETSTAT)。可以查看電腦上所有開放的TCP端口列表,如下:
Get-NetTcpConnection -State Listen | Select-Object LocalAddress,LocalPort| Sort-Object -Property LocalPort | Format-Table
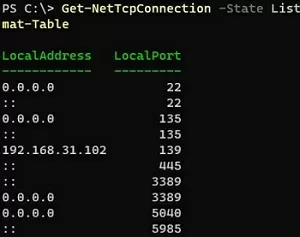

您還可以使用 Get-NetTCPConnection cmdlet 列出活動的 TCP/IP 連接。
如果您想找出哪個程序(進程)正在偵聽計算機上的特定端口,請使用以下命令(其中 443 是您要檢查的端口號):
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 443).OwningProcess | ft Id, ProcessName, UserName, Path







![如何将数据从 iQOO 传输到 iPhone [2026 更新]](https://tips.pfrlju.com/tech/enda/wp-content/uploads/cache/2025/12/iqoo-to-iphone.jpg)






