使用 PowerShell 和 GPO 清除 Windows (RDS) 上用戶配置文件中的緩存和臨時文件
Windows Server RDS 場管理員經常面臨由於大量用戶數據而導致系統驅動器空間不足的問題。本文向您展示如何使用 PowerShell 和組策略自動清理 Windows 上用戶配置文件中的回收站、下載、臨時和緩存文件夾。
內容:
您可以使用內置的存儲感自動刪除 Windows Server 2019/2022 和 Windows 10/11 上的舊文件和臨時文件的功能。它具有特殊的 GPO 選項,允許您清理臨時文件夾和下載文件夾。

Windows用戶如何清空回收站?
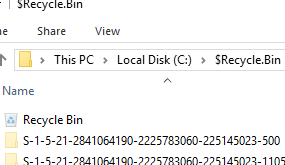
默認情況下,回收站文件夾 ($Recycle.Bin) 對於已刪除的文件在 Windows 主機上啟用。在 RDS 服務器上的該目錄(以用戶的 SID 作為名稱)中為每個用戶創建單獨的回收站文件夾。隨著時間的推移,您會發現所有用戶的回收站中的文件總大小將佔用 RDS 主機上大量的磁盤空間。

Windows 中回收站的默認大小約為磁盤大小的 5%。您可以在每個驅動器的屬性中更改回收站的最大大小。在這裡您還可以使用以下命令完全禁用回收站不要將文件移至回收站選項。但是,這只會更改當前用戶的回收站設置。
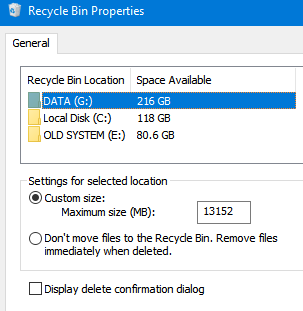

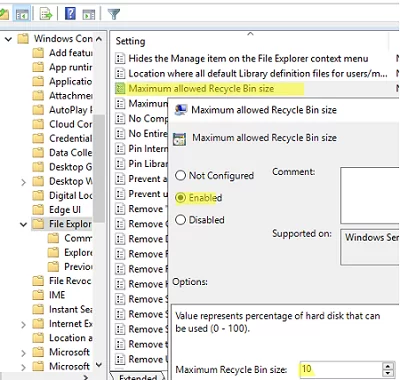
您可以為用戶設置最大回收站大小允許的最大回收站大小用戶配置 -> 管理模板 -> Windows 組件 -> 文件資源管理器下的 GPO 選項。最大回收站大小設置為磁盤大小的百分比。將此值設置為 0 將禁用所有驅動器上的回收站。

要清除 Windows 中的回收站,您可以使用清除回收站cmdlet(在 Windows 10 上的 PowerShell 5.1 及更高版本中可用)。為了在沒有提示的情況下清空回收站,請運行以下命令:
Clear-RecycleBin -Force
如果在RDS主機上以普通用戶身份運行該命令,則只會清除當前用戶的回收站。您可以將此命令添加到 GPO 註銷腳本中,以便在用戶註銷時清除回收站:
建議閱讀:如何使用軟件限制策略 GPO 禁用 PowerShell
%windir%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe -NoProfile -Command Clear-RecycleBin -Confirm:$false
對於以前版本的Windows(使用舊版本的PowerShell),您可以使用以下代碼來清理RecycleBin:
$Shell = New-Object -ComObject Shell.Application
$RecycleBin = $Shell.Namespace(0xA)
$RecycleBin.Items() | %{Remove-Item $_.Path -Recurse -Confirm:$false}
使用 PowerShell 清除用戶配置文件中的緩存、臨時文件夾和下載文件夾
讓我們考慮使用 PowerShell 腳本來清理 Windows Server RDS 或運行 Windows 10/11 的桌面計算機上的用戶配置文件中的 Temp、Downloads 和其他一些臨時文件夾。
腳本評論:
- 在此示例中,我們將刪除早於14下載文件夾中的天數(您可以更改此選項)。其他帶有緩存和臨時文件的文件夾將完全清空;
- 該腳本在當前用戶上下文中運行(當用戶從 Windows 註銷並作為 GPO 註銷腳本運行時,該腳本會刪除舊文件);如果在 RDS 環境中使用,請確保用戶單擊“註銷/登錄”按鈕來結束其會話。我們還建議配置 RDS 會話超時,以便在一段時間不活動後自動結束會話。
- 有關已刪除文件的所有信息將保存到文本日誌文件中(您可以在測試用戶上調試腳本後禁用此功能);
- 它還將清理 RDP 連接歷史記錄和緩存;
- 用戶配置文件中的 Windows 錯誤報告 (WER) 文件夾已清理;
- 腳本中註釋掉了清除 Google Chrome 緩存的行。如果您的用戶使用它並且 Chrome 緩存佔用大量空間,請取消註釋帶有路徑的行;
- 您可以添加額外的操作來檢查清理前後用戶配置文件文件夾的當前大小(它可以讓您獲得更準確的信息,但需要一些時間)。或者您可以簡單地檢查前後的可用磁盤空間(很快就能完成)。
# You can use this script to clean folders in a user profile (cache, temp, downloads, google chrome cache) on RDS hosts, VDIs, or workstations
# Run the PowerShell script under a commaon user account (no administrator privileges are required). Only temporary files and the current user's cache are deleted.
# You can run this script via GPO (logoff script) or with the Task Scheduler
# Test the script in your environment and then remove the WhatIf option to permanently delete files
$Logfile = "$env:USERPROFILEcleanup_profile_script.log"
$OldFilesData = (Get-Date).AddDays(-14)
# Complete cleanup of cache folders
[array] $clear_paths = (
'AppDataLocalTemp',
'AppDataLocalMicrosoftTerminal Server ClientCache',
'AppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsWER',
'AppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsAppCache',
'AppDataLocalCrashDumps'
#'AppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultCache',
#'AppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultCache2entries',
#'AppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultCookies',
#'AppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultMedia Cache',
#'AppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultCookies-Journal'
)
# Folders where only old files should be removed
[array] $clear_old_paths = (
'Downloads'
)
function WriteLog {
Param ([string]$LogString)
$Stamp = (Get-Date).ToString("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss")
$LogMessage = "$Stamp $LogString"
Add-content $LogFile -value $LogMessage
}
WriteLog "Starting profile cleanup script"
# If you want to clear the Google Chrome cache folder, stop the chrome.exe process
$currentuser = $env:UserDomain + ""+ $env:UserName
WriteLog "Stopping Chrome.exe Process for $currentuser"
Get-Process -Name chrome -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Where-Object {$_.SI -eq (Get-Process -PID $PID).SessionId} | Stop-Process
Start-Sleep -Seconds 5
# Clean up cache folders
ForEach ($path In $clear_paths) {
If ((Test-Path -Path "$env:USERPROFILE$path") -eq $true) {
WriteLog "Clearing $env:USERPROFILE$path"
Remove-Item -Path "$env:USERPROFILE$path" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue -WhatIf -Verbose 4>&1 | Add-Content $Logfile
}
}
# Delete old files
ForEach ($path_old In $clear_old_paths) {
If ((Test-Path -Path "$env:USERPROFILE$path_old") -eq $true) {
WriteLog "Clearing $env:USERPROFILE$path_old"
Get-ChildItem -Path "$env:USERPROFILE$path_old" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Where-Object {($_.LastWriteTime -lt $OldFilesData)} | Remove-Item -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue -WhatIf -Verbose 4>&1 | Add-Content $Logfile
}
}
WriteLog "End profile cleanup script"
同樣,您可以將用戶配置文件中要清除的其他文件夾添加到$clear_paths。
請參閱我的 GitHub 存儲庫以獲取該腳本的完整版本:https://github.com/maxbakhub/winposh/blob/main/RDS/CleanupUserProfile.ps1。
此 PowerShell 腳本可以在用戶的 RDP 服務器會話結束時運行。分配腳本的最簡單方法是使用註銷 GPO 策略。
- 創建一個新的 GPO 並將其分配給您的 RDS 主機所在的組織單位 (OU);
- 啟用選項配置用戶組策略環回處理方式。這是將“用戶”部分的設置應用到計算機所必需的;
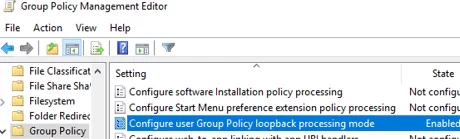
 有關詳細信息,請參閱為什麼組策略未應用於計算機/用戶。
有關詳細信息,請參閱為什麼組策略未應用於計算機/用戶。 - 將 PowerShell 腳本文件複製到域控制器上的 Net 登錄文件夾 (
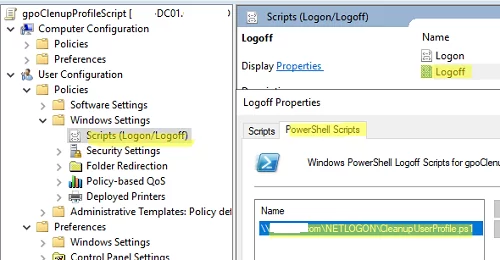
\woshub.comnetlogonCleanupUserProfile.ps1);您可以使用證書對 PowerShell 腳本代碼進行簽名,以防止其受到未經授權的修改。 - 轉到 GPO 部分用戶配置 -> 策略 -> Windows 設置 -> 腳本 -> 註銷。打開PowerShell 腳本選項卡並在 Netlogon 中添加 PS1 文件的 UNC 路徑;
 從 Windows 註銷用戶以應用新的 GPO 設置;
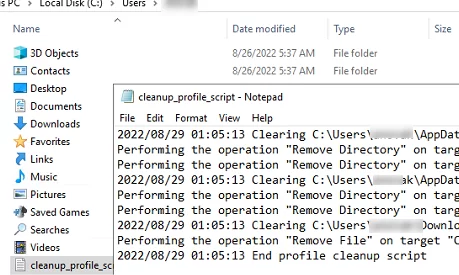
從 Windows 註銷用戶以應用新的 GPO 設置;- 當結束 RDS 服務器上的用戶會話時,指定的文件夾將被自動清除。您可以在用戶配置文件的文本日誌文件中查看已刪除文件和文件夾的列表。

您還可以使用以下方法來管理 Windows Server RDS 服務器上的用戶配置文件大小:
- 如何刪除舊的用戶配置文件?
- 啟用 NTFS 磁盤配額
此處討論的用戶文件夾清理方法可應用於本地存儲的用戶配置文件和 Windows Server RDSH 上的用戶配置文件磁盤或 FSlogix 配置文件容器。